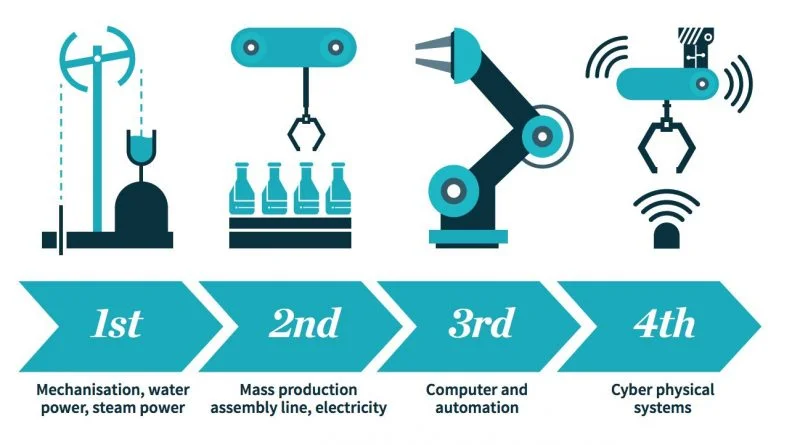
Introduction: At the beginning of the twenty-first century, humanity is on the verge of a technological revolution never before seen. The convergence of the digital, physical, and biological domains has brought about a new era known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), which has completely changed the way we work, live, and interact. Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are the cornerstone of innovation driving extraordinary gains across industries globally, and they are fundamental to this transformative period. Fundamentally, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is a paradigm shift marked by the convergence of multiple technologies, such as blockchain, robotics, Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and 3D printing. The distinctions between the digital, biological, and physical domains are becoming more hazy due to this blending of the two.
Cyber-Physical Systems, a pivotal component of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, embody the integration of computational algorithms and physical processes, enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and control of interconnected systems. These systems leverage advanced sensors, actuators, and communication networks to bridge the gap between the virtual and physical worlds, facilitating seamless interaction and decision-making in diverse domains such as manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, and infrastructure.
One of the most profound impacts of Industrial Revolution 4.0 and Cyber-Physical Systems lies in their ability to enhance operational efficiency, productivity, and resource optimization across industries. Through the deployment of smart sensors and interconnected devices, organizations can collect vast amounts of data from disparate sources, enabling predictive maintenance, optimized production processes, and just-in-time inventory management. Consequently, businesses can minimize downtime, reduce costs, and enhance overall competitiveness in an increasingly dynamic and interconnected global landscape.
Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms within Cyber-Physical Systems empowers autonomous decision-making and adaptive behavior, revolutionizing traditional manufacturing paradigms. Smart factories equipped with CPS technologies can autonomously adjust production schedules, optimize energy consumption, and self-diagnose equipment failures, thereby streamlining operations and maximizing productivity while minimizing human intervention.
In addition to driving operational efficiency, Industrial Revolution 4.0 and Cyber-Physical Systems hold immense potential for fostering innovation, creativity, and entrepreneurship on a global scale. The democratization of technology and the proliferation of digital platforms have lowered barriers to entry, enabling individuals and small businesses to leverage advanced tools and resources to develop and commercialize groundbreaking solutions. From 3D-printed prosthetics to personalized medicine and smart cities, the transformative power of CPS-driven innovation is reshaping industries and revolutionizing the way we address societal challenges.
Moreover, the advent of Cyber-Physical Systems has profound implications for the future of work, necessitating a paradigm shift in education, skills development, and workforce readiness. As automation and AI continue to augment and redefine traditional job roles, there is an urgent need for individuals to acquire digital literacy, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills to thrive in the digital economy. By fostering a culture of lifelong learning and adaptability, societies can harness the potential of Industrial Revolution 4.0 to create inclusive, equitable, and sustainable opportunities for all.
In conclusion, the role of Industrial Revolution 4.0 and Cyber-Physical Systems in the 21st century cannot be overstated. These transformative forces are reshaping industries, economies, and societies at an unprecedented pace, unlocking new frontiers of innovation and human potential. By embracing the opportunities presented by CPS-driven technologies and fostering collaboration across disciplines and sectors, we can navigate the complexities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution and build a more resilient, prosperous, and sustainable future for generations to come.
What are Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) and how do they relate to the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR)?
Answer: CPS are systems that integrate physical processes with computational algorithms, enabling real-time monitoring and control. They play a central role in 4IR by bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds, driving innovation and transforming traditional industries.
What are some examples of Cyber-Physical Systems in the 21st century?
Answer: Examples of CPS include smart manufacturing systems, autonomous vehicles, smart grids, wearable health monitors, and intelligent infrastructure. These systems leverage advanced sensors, actuators, and communication networks to enable seamless interaction between physical and digital environments.
How do Industrial Revolution 4.0 and Cyber-Physical Systems impact operational efficiency and productivity?
Answer: 4IR and CPS enhance operational efficiency by enabling real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making. Through predictive maintenance, optimized production processes, and autonomous control, organizations can minimize downtime, reduce costs, and maximize productivity across industries.
What are the implications of Industrial Revolution 4.0 and Cyber-Physical Systems for the future of work?
Answer: 4IR and CPS are reshaping the nature of work by automating routine tasks and augmenting human capabilities with AI and robotics. While this may lead to job displacement in some sectors, it also creates new opportunities for skills development, entrepreneurship, and innovation in emerging fields.
How can societies harness the potential of Cyber-Physical Systems to address societal challenges?
Answer: By fostering collaboration between government, industry, academia, and civil society, societies can leverage CPS-driven technologies to address pressing challenges such as healthcare, transportation, energy, and environmental sustainability. Embracing a holistic approach to innovation and technology adoption can unlock the transformative power of CPS for the benefit of all.